How to operate a drone safely and effectively is more than just mastering the controls; it’s about understanding the technology, adhering to regulations, and prioritizing safety. This guide delves into the essential steps, from pre-flight checks and understanding airspace restrictions to mastering flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies with your drone.
From basic controls to advanced maneuvers, we’ll explore the intricacies of drone operation, offering practical tips and troubleshooting advice. Whether you’re a beginner taking your first flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to operate your drone responsibly and enjoyably.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before embarking on any drone flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful operation. This involves a series of inspections and confirmations to guarantee the drone’s airworthiness and your compliance with all relevant regulations. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to property, and legal repercussions.
Drone Inspection
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection covers several key areas of the drone. This ensures all components are functioning correctly and the drone is ready for flight.
| Component | Check | Component | Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for damage, cracks, or loose fittings. Ensure they are securely attached. | Battery | Check battery level and ensure it is securely connected. Inspect for any damage or swelling. |
| Motors | Visually inspect for any signs of damage or wear. Check for smooth rotation by gently spinning each motor. | Camera | Confirm the camera is securely mounted and functioning correctly. Check lens for any smudges or obstructions. |
| Gimbal (if applicable) | Ensure the gimbal moves smoothly and locks securely in position. Check for any unusual noises or vibrations. | Airframe | Inspect the drone’s body for any damage, cracks, or loose parts. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. The number of satellites locked should be sufficient for stable flight. | Remote Controller | Check the batteries are sufficiently charged and that the controller is properly paired with the drone. |
Local Regulations and Airspace Restrictions
Understanding and adhering to local drone regulations and airspace restrictions is paramount for safe and legal drone operation. These regulations vary by country, region, and even specific locations. Ignorance of these rules can lead to fines or even legal action.
Common restrictions include no-fly zones near airports, stadiums, and other sensitive areas. Height restrictions are also frequently imposed, limiting how high the drone can fly. Some areas may also restrict drone operation altogether. Always check the relevant authorities’ websites or apps (such as B4UFLY in the US or similar apps in other countries) before flying.
Emergency Procedures
Preparing for potential emergencies is crucial for safe drone operation. Knowing how to react to unexpected situations can prevent accidents and minimize damage.
- Loss of Signal: If the signal is lost, the drone will typically enter a Return-to-Home (RTH) mode, returning automatically to its takeoff point. However, be prepared to visually locate the drone and manually guide it back if necessary. Practice this maneuver beforehand.
- Low Battery: Most drones provide low-battery warnings. Immediately initiate the RTH function and land the drone safely. Never push the drone to its absolute limit.
- Unexpected Malfunction: If a motor fails or another malfunction occurs, immediately attempt a controlled landing. Prioritize safety and land in a clear, open area.
Drone Controls and Operation
Successfully operating a drone requires understanding its controls and mastering the techniques for safe takeoff and landing. Practice is key to developing proficiency and confidence.
Takeoff and Landing Procedures
The following steps provide a safe and reliable method for takeoff and landing.
- Perform a pre-flight check.
- Power on the remote controller first, then the drone.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition (if applicable).
- Slowly lift off vertically, maintaining a steady ascent.
- During flight, monitor battery level and maintain a safe distance from obstacles.
- For landing, slowly descend vertically, maintaining a steady rate.
- Power off the drone, then the remote controller.
Drone Remote Control Functions, How to operate a drone
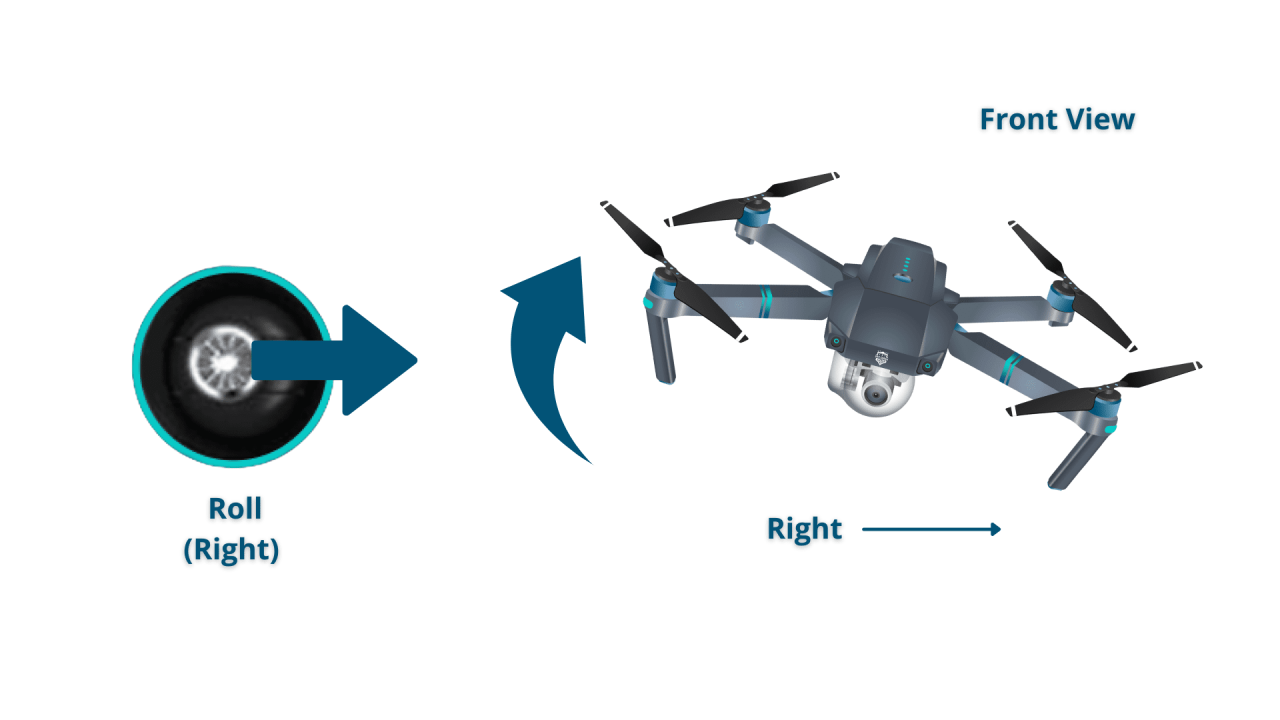
A standard drone remote controller typically utilizes joysticks, buttons, and switches to control various aspects of the drone’s flight and camera operation. Understanding these functions is essential for safe and effective control.
| Control | Action | Control | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left Joystick (Vertical) | Ascend/Descend | Right Joystick (Vertical) | Pitch (tilt forward/backward) |
| Left Joystick (Horizontal) | Yaw (rotate left/right) | Right Joystick (Horizontal) | Roll (tilt left/right) |
| Buttons | Various functions, including Return-to-Home (RTH), camera controls, and flight mode selection | Dials | Adjust camera settings, such as zoom and focus |
Camera Angle and Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera angles and settings during flight allows for creative aerial photography and videography. Different shots can add visual interest and tell a story more effectively.
Examples include: establishing shots (wide shots showing the overall scene), medium shots (showing more detail), close-up shots (emphasizing specific elements), and dynamic shots (using movement to create visual interest). Adjusting settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO allows for control over depth of field, motion blur, and image brightness.
Navigation and Flight Techniques
Effective drone navigation relies on understanding different flight modes and employing appropriate techniques for various missions. This section explores different methods of navigation and Artikels a simple flight plan.
Learning to fly a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to safely and effectively navigate the skies. Remember, responsible operation is key to enjoying this exciting technology.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Beginner mode often limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more aggressive maneuvers. GPS mode uses satellite data for precise positioning and autonomous functions.
Sample Flight Plan for Aerial Photography
This plan Artikels a simple aerial photography mission focusing on a park.
- Takeoff from a designated area.
- Ascend to a pre-determined altitude.
- Fly along a pre-planned route, capturing establishing shots of the park.
- Capture medium shots of specific features, such as a pond or playground.
- Perform some orbiting maneuvers around key points of interest.
- Descend and land safely.
Drone Navigation Methods
GPS, visual, and manual navigation methods offer different levels of precision and control. GPS provides precise positioning and enables autonomous flight features. Visual navigation relies on the pilot’s observation of the drone’s position relative to its surroundings. Manual navigation offers maximum control but requires more skill and experience.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding key aspects of photography and videography, including framing, composition, and lighting. This section explores techniques for optimizing image quality.
Tips and Techniques
Achieving professional-looking aerial footage involves careful consideration of framing, composition, and lighting. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and other compositional techniques can enhance the visual appeal of your images. Proper lighting, whether natural or artificial, plays a vital role in the overall quality of your shots.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjusting camera settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO is crucial for optimizing image quality in various lighting conditions. Aperture affects depth of field, shutter speed controls motion blur, and ISO influences image sensitivity to light.
Drone Camera Features Comparison
| Feature | Capability | Feature | Capability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Size | Larger sensors generally produce higher quality images with better low-light performance. | Resolution | Higher resolution means more detail in the images and videos. |
| Aperture Range | A wider aperture range allows for better control over depth of field and low-light performance. | Video Recording Capabilities | Consider frame rates, resolutions, and codecs supported for video recording. |
| Gimbal Stabilization | A high-quality gimbal helps reduce camera shake and produce smoother footage. | Zoom Capability | Optical zoom offers better image quality compared to digital zoom. |
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its continued safe operation. This section Artikels the necessary steps.
Powering Down and Storing
Safely powering down and storing your drone after a flight is crucial to protect its components and prevent accidental damage. Always power down the drone first, then the remote controller. Store the drone in a clean, dry place, away from extreme temperatures.
Routine Maintenance

Regular maintenance helps to keep your drone in top condition and prevents potential problems. This includes inspecting and cleaning the propellers, motors, and airframe.
- Inspect propellers for damage and replace as needed.
- Clean the drone body and propellers with a soft cloth.
- Check for loose screws or connections and tighten as necessary.
- Inspect the gimbal (if applicable) for smooth operation.
- Store the drone and accessories in a protective case.
Post-Flight Checklist
| Task | Completed |
|---|---|
| Power down drone and remote | |
| Inspect drone for damage | |
| Clean drone and propellers | |
| Charge batteries | |
| Download flight data | |
| Store drone and accessories |
Understanding Drone Batteries and Flight Time
Proper battery care and understanding factors affecting flight time are critical for safe and efficient drone operation. This section details battery management and flight time estimation.
Battery Care and Handling
Drone batteries require careful handling and charging to ensure optimal performance and longevity. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow charging instructions precisely. Avoid overcharging or discharging the batteries, and store them in a cool, dry place.
Factors Affecting Flight Time
| Factor | Effect on Flight Time |
|---|---|
| Wind Speed | Higher wind speeds reduce flight time due to increased energy consumption. |
| Payload Weight | Heavier payloads (e.g., larger cameras) reduce flight time. |
| Temperature | Extreme temperatures (both hot and cold) can negatively impact battery performance and reduce flight time. |
| Battery Age | Older batteries generally have reduced capacity and shorter flight times. |
Estimating Flight Time

Estimating flight time involves considering the drone’s battery capacity and the factors discussed above. Manufacturers typically provide estimated flight times under ideal conditions. However, these estimates should be adjusted based on real-world conditions, such as wind and temperature.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Understanding common drone problems and their solutions is essential for maintaining operational readiness. This section provides troubleshooting guidance for common issues.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Various issues can arise during drone operation. Knowing how to address them efficiently can minimize downtime and prevent accidents.
- GPS Signal Loss: Ensure clear skies and sufficient satellites are acquired before takeoff. Relocate to an area with better GPS reception if necessary.
- Motor Failures: Inspect motors for damage or obstructions. Replace faulty motors as needed.
- Camera Malfunctions: Check camera connections and settings. If the problem persists, the camera may require replacement.
- Low Battery Warning: Initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) immediately and land the drone safely.
- Controller Connectivity Issues: Check battery levels on both the drone and the controller. Ensure proper pairing and try restarting both devices.
Diagnosing and Resolving Technical Issues
Troubleshooting involves systematically identifying the root cause of the problem. This may involve checking connections, inspecting components for damage, or consulting the drone’s manual or online resources. Safety should always be the top priority when diagnosing and resolving technical issues.
Operating a drone responsibly requires a blend of technical skill, regulatory awareness, and a commitment to safety. By diligently following pre-flight procedures, mastering the controls, and understanding airspace limitations, you can unlock the exciting possibilities of aerial photography and videography. Remember, consistent practice and a proactive approach to maintenance are key to ensuring both your safety and the longevity of your drone.
So, take to the skies with confidence, capture breathtaking footage, and enjoy the adventure!
FAQ Overview
What is the legal age to operate a drone?
Legal age restrictions vary by location. Check your local laws and regulations.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements depend on your location and drone weight. Consult your country’s aviation authority website.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a “return to home” (RTH) function. If that fails, attempt to manually regain control. If unsuccessful, contact local authorities if it poses a safety risk.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrate your compass before each flight, especially in areas with magnetic interference.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to safe navigation. Learning how to control the drone’s altitude, speed, and direction is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This knowledge is essential for both recreational and professional drone pilots, ensuring safe and effective flights.
Ultimately, responsible drone operation is paramount for both personal safety and respecting airspace regulations.
What type of insurance is recommended for drone operation?
Liability insurance is highly recommended to cover potential damages or injuries.
